RBI’s Regulatory Framework for Microfinance Companies
Microfinance plays a crucial role in providing financial assistance to underserved individuals and small businesses that lack access to conventional banking. To maintain financial stability, ensure transparency, and protect borrowers from unethical lending practices, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) oversees the operations of microfinance institutions (MFIs).
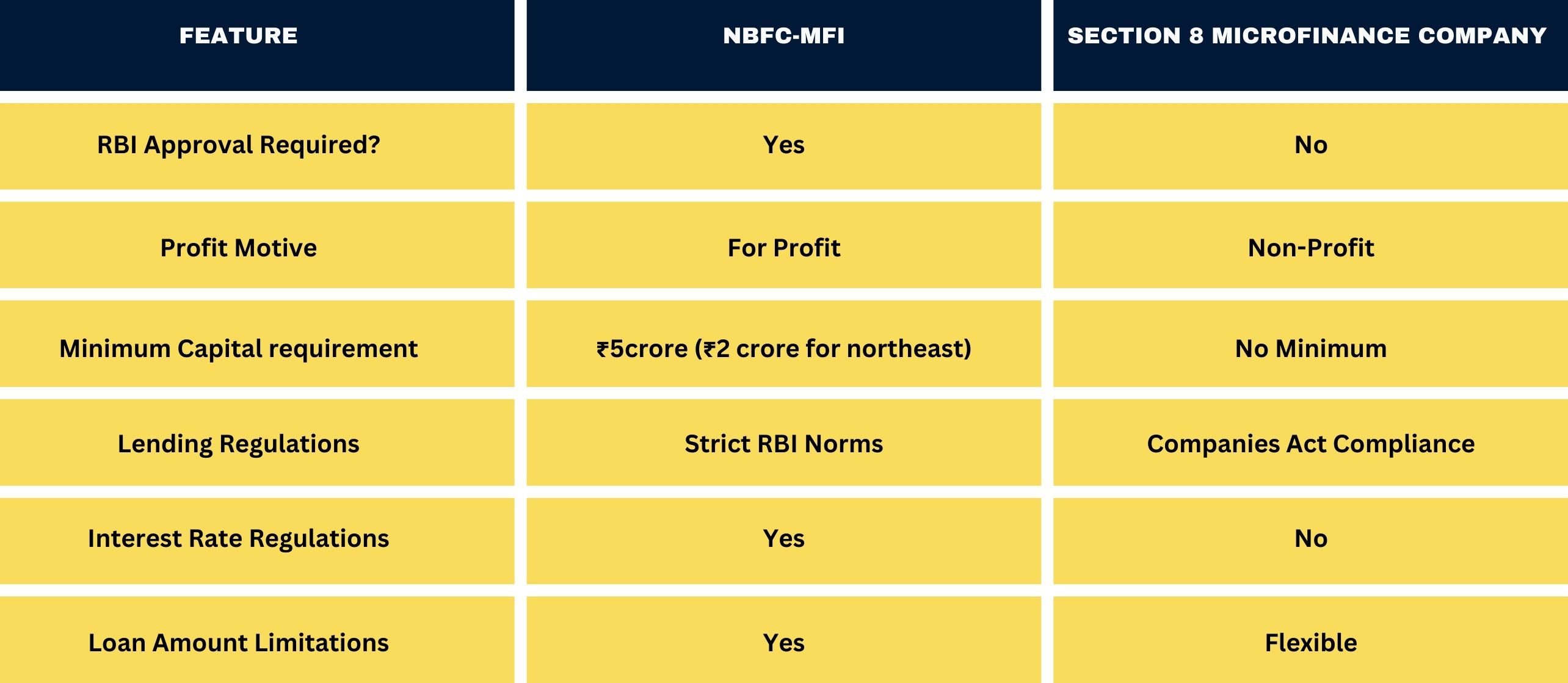
The microfinance company registration process in Hindi varies depending on the type of institution. Non-Banking Financial Company-Microfinance Institutions (NBFC-MFIs) must obtain an RBI license and adhere to strict regulations. On the other hand, Section 8 microfinance company registration function as non-profit entities and do not require RBI approval, though they must comply with the Companies Act, 2013.
RBI’s regulatory responsibilities include licensing and registration, setting minimum capital requirements, and enforcing interest rate caps to prevent borrower exploitation. For NBFC-MFIs, the RBI mandates a minimum Net Owned Fund (NOF) of ₹5 crore (₹2 crore for northeastern states) to ensure financial sustainability. Interest rate regulations ensure that lending remains fair and within prescribed limits.
Additionally, RBI enforces borrower protection measures to prevent unethical recovery practices. MFIs must disclose loan terms transparently and follow responsible collection procedures. The central bank also supervises these institutions through periodic audits and compliance checks, ensuring adherence to financial regulations.
While microfinance Section 8 companies operate with greater flexibility, they must still follow ethical lending practices. The RBI indirectly influences these companies through broader financial regulations. Challenges in microfinance regulation include high compliance costs, borrower over-indebtedness, and loan defaults in economically unstable regions.
Despite challenges, RBI continues to refine its policies to enhance financial inclusion and borrower protection. Understanding the microfinance company registration process in Hindi and RBI’s regulations is vital for businesses looking to enter the sector and contribute to responsible financial growth in India.

Introduction
Microfinance plays a crucial role in providing financial services to low-income individuals and small businesses that lack access to traditional banking. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) regulates microfinance companies to ensure financial stability, protect borrowers from exploitation, and maintain transparency in lending operations. This blog explores the role of RBI in regulating microfinance institutions and covers key aspects, including microfinance company registration process in Hindi, Section 8 company microfinance, microfinance Section 8 company, and Section 8 microfinance.
Understanding Microfinance Companies
Microfinance companies are financial institutions that provide small loans to individuals, self-help groups, and small enterprises. These loans are designed to promote entrepreneurship and economic growth among marginalized sections of society. Microfinance institutions (MFIs) operate in two primary categories:
- Non-Banking Financial Company – Microfinance Institution (NBFC-MFI): These institutions require RBI approval to operate and follow strict financial regulations.
- Section 8 Microfinance Company: A non-profit entity that provides microloans without RBI approval but must comply with the Companies Act, 2013
Microfinance Company Registration Process in Hindi
For those looking to understand the microfinance company registration process in Hindi, it is essential to note that the process involves several legal and regulatory steps. The registration process differs for Section 8 microfinance companies and NBFC-MFIs While a Section 8 company microfinance does not require RBI approval, an NBFC-MFI must undergo a stringent regulatory process.

Role of RBI in Regulating Microfinance Companies
The RBI plays a critical role in regulating microfinance companies to ensure responsible lending, financial stability, and consumer protection. Here are the key responsibilities of the RBI in the microfinance sector:
1. Licensing and Registration
RBI mandates that any microfinance institution intending to operate as an NBFC-MFI must obtain an RBI license. The microfinance company registration process in Hindi follows a structured approach that includes company incorporation, securing the required minimum capital, and applying for an NBFC license.
2. Setting Capital Requirements
For an NBFC-MFI, the RBI has set a minimum Net Owned Fund (NOF) requirement of ₹5 crore (₹2 crore for northeastern states). This capital ensures that microfinance companies have adequate financial resources to sustain operations.
3. Interest Rate and Loan Limits Regulation
To prevent exploitation and ensure fair lending, RBI regulates the interest rates charged by microfinance institutions. NBFC-MFIs must adhere to a margin cap, ensuring that the difference between borrowing and lending rates remains within prescribed limits.
4. Borrower Protection and Fair Practices
RBI mandates fair lending practices to protect borrowers from unethical collection methods. Microfinance companies must provide complete loan information, avoid coercive recovery methods, and follow transparent pricing policies.
5. Monitoring and Supervision
The RBI continuously monitors microfinance institutions through compliance audits, financial reporting, and regulatory inspections. NBFC-MFIs must submit periodic reports on their financial health and loan portfolios.
6. Regulation of Loan Repayment Tenure
The RBI sets guidelines on loan repayment tenures to prevent over-indebtedness among borrowers. It ensures that repayment structures remain feasible and do not burden low-income borrowers.
7. Section 8 Microfinance Regulation
While Section 8 microfinance companies are exempt from RBI licensing, they must comply with the Companies Act, 2013 and follow ethical lending standards. The RBI indirectly influences these institutions through financial sector regulations.
8. Addressing Customer Complaints and Dispute Resolution
The RBI has established grievance redressal mechanisms to handle complaints against microfinance institutions. Borrowers can approach the Ombudsman or RBI if they face unfair lending practices.
Comparison: NBFC-MFI vs. Section 8 Microfinance Company
Microfinance Section 8 Company and Its Advantages
A microfinance Section 8 company operates as a non-profit entity dedicated to financial inclusion. Some of the key advantages include:
- No RBI approval required.
- Lower compliance costs compared to NBFC-MFIs.
- Greater flexibility in lending terms.
- Exemption from certain taxes and legal obligations.
Challenges in Microfinance Regulation
Despite RBI’s robust regulatory framework, microfinance institutions face several challenges:
- High operational costs due to compliance and reporting requirements.
- Over-indebtedness of borrowers due to multiple loans from different lenders.
- The risk of loan defaults, particularly in economically volatile regions.
- Limited funding sources for small microfinance institutions.
Future of RBI Regulation in Microfinance
The RBI continues to evolve its regulatory policies to enhance financial inclusion while maintaining financial stability. Some anticipated developments include:
- Introduction of more borrower-friendly policies.
- Enhanced digital lending regulations to curb fraudulent practices.
- Strengthening NBFC-MFI governance structures.
- Increasing financial literacy programs to educate borrowers on responsible borrowing.
Conclusion
The RBI plays a pivotal role in regulating microfinance companies, ensuring fair lending practices, financial stability, and borrower protection. While NBFC-MFIs must comply with stringent RBI norms, a Section 8 microfinance company operates with greater flexibility under the Companies Act. Understanding the microfinance company registration process in Hindi and adhering to RBI regulations are crucial for businesses looking to enter the microfinance sector. By maintaining a balance between regulatory compliance and financial inclusion, RBI helps promote sustainable microfinance practices in India.
Why Choose Vakilkaro for Microfinance and Other Legal Services?
Vakilkaro is a trusted legal services provider known for its expertise in company registration, compliance, and financial advisory services. Whether you are looking to establish a Section 8 microfinance company, complete the microfinance company registration process in Hindi, or need assistance with RBI regulations, Vakilkaro ensures a seamless and hassle-free experience.
With a team of experienced professionals, Vakilkaro offers end-to-end guidance on NBFC-MFI registration, Section 8 company incorporation, and RBI compliance. Their services include document preparation, legal consultation, and post-registration compliance to ensure businesses operate within regulatory frameworks.
Vakilkaro’s expertise extends beyond microfinance, covering GST registration trademark registration tax advisory, corporate law, and intellectual property protection. Their commitment to transparency, accuracy, and efficiency makes them the preferred choice for businesses seeking legal and financial solutions. By choosing Vakilkaro, clients benefit from personalized support, reduced compliance risks, and a smooth legal process, ensuring long-term success in their financial ventures.