Understanding RBI Guidelines for Microfinance Companies in India
Microfinance companies play a crucial role in fostering financial inclusion by providing small loans to individuals and businesses that lack access to conventional banking services. To regulate these institutions and ensure ethical lending practices, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has established specific guidelines. These regulations aim to maintain transparency, protect borrowers, and promote financial stability within the sector.
For those looking to start a microfinance business, understanding RBI regulations is essential. The guidelines cover various aspects, including Section 8 microfinance company registrationmicrofinance registration, micro finance company registration, NBFC registration, andNBFC for sale Compliance with these norms helps microfinance institutions (MFIs) operate legally while safeguarding borrower interests.
Microfinance companies in India fall into two main categories: NBFC-Microfinance Institutions (NBFC-MFIs) and Section 8 Microfinance Companies. NBFC-MFIs operate as for-profit entities and must obtain RBI approval, adhere to strict compliance norms, and meet capital requirements. Section 8 Microfinance Companies, on the other hand, function as non-profit organizations, offering financial assistance without a profit motive. These companies do not require RBI approval but must comply with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) regulations.
RBI’s guidelines focus on key areas such as loan amount limits, interest rates, repayment structures, fair lending practices, and reporting to credit bureaus. Additionally, businesses considering NBFC for sale must comply with RBI’s due diligence and ownership transfer regulations.
Following RBI regulations ensures that microfinance companies operate transparently, mitigate risks, and contribute to financial inclusion. Whether establishing a new microfinance institution or purchasing an existing NBFC, adhering to RBI guidelines is crucial for long-term success and regulatory compliance.
Introduction
Microfinance companies play a crucial role in bridging the financial gap by providing small-ticket loans to individuals and businesses that do not qualify for traditional bank loans. These institutions empower low-income individuals, especially in rural and semi-urban areas, by giving them access to credit, which helps them start businesses, expand existing ventures, and meet essential financial needs. The Reserve Bank of India(RBI) has established a regulatory framework to govern microfinance institutions, ensuring they operate transparently while protecting borrowers from exploitative practices.
If you are considering starting a microfinance company in India, it is essential to understand the regulatory landscape. The RBI guidelines are designed to bring stability to the sector, maintain fair lending practices, and prevent over-indebtedness among borrowers. These regulations apply to different types of microfinance institutions, including NBFC-Microfinance Institutions (NBFC-MFIs) and Section 8 Microfinance Companies.
Microfinance institutions in India are broadly classified into two categories:
- NBFC-Microfinance Institutions (NBFC-MFIs): These are for-profit microfinance companies that require RBI approval and must comply with stringent regulations related to capital adequacy, interest rate caps, borrower eligibility, and reporting requirements.
- Section 8 Microfinance Companies: These operate as non-profit organizations and do not require RBI approval. They function under the Companies Act, 2013, and follow the guidelines set by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
The RBI’s framework ensures that microfinance companies function ethically, preventing predatory lending and excessive interest rates. Whether you are looking for Section 8 microfinance company registration, microfinance registration, micro finance companyregistration, NBFC registrationor exploring NBFC for sale, adhering to RBI norms is crucial. A well-regulated microfinance company not only ensures legal compliance but also fosters trust among borrowers, promoting financial inclusion on a large scale.
Understanding Microfinance Companies
Microfinance institutions (MFIs) offer financial services, primarily microloans, to low-income individuals and small businesses that do not qualify for traditional bank loans. These loans help borrowers generate income, support their livelihoods, and improve their quality of life. In India, microfinance companies are broadly classified into two categories:
- Non-Banking Financial Company – Microfinance Institution (NBFC-MFI): These are for-profit organizations that require RBI approval and adhere to strict financial regulations.
- Section 8 Microfinance Company: A non-profit organization that provides financial assistance without a profit motive and does not require RBI approval.
Key RBI Guidelines for Microfinance Companies
The RBI has issued comprehensive guidelines to regulate microfinance companies, ensuring they operate in a structured manner while protecting borrowers from unethical lending practices. These regulations include:
1. Registration and Compliance
- NBFC-MFIs must be registered with the RBI under the NBFC registration category.
- To qualify as an NBFC-MFI, at least 85% of net assets must be in the form of microfinance loans.
- Section 8 microfinance company registration does not require RBI approval but must comply with the Companies Act, 2013 and adhere to guidelines set by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
2. Capital Requirements
- NBFC-MFIs must have a minimum net owned fund (NOF) of ₹5 crore, except in the Northeastern states, where it is ₹2 crore.
- Section 8 microfinance companies have no minimum capital requirements, making them a cost-effective option for social entrepreneurs.
3. Loan Amount and Interest Rates
- For an NBFC-MFI, the maximum loan amount per borrower should not exceed:
- ₹75,000 in the first cycle.
- ₹1,25,000 in subsequent cycles.
- Interest rates should not exceed the cost of funds plus a margin cap of 10% to 12%.
- NBFC-MFIs must follow a uniform and transparent interest rate calculation method and disclose it to borrowers.
4. Repayment and Tenure
- The repayment period for loans exceeding ₹30,000 must be at least 24 months.
- Borrowers should have the flexibility of prepayment without penalty.
- Weekly, fortnightly, or monthly repayment structures should be followed based on borrower preference.
5. Fair Practices Code
- MFIs must not use coercive collection methods and should follow ethical lending practices.
- Loan agreements should be clear, concise, and in a language understood by the borrower.
- Transparency in charges and penalties is mandatory to protect borrowers from hidden costs.
6. Credit Bureau Reporting
- MFIs must report borrower details to credit bureaus such as CIBIL, Equifax, Experian, or CRIF Highmark.
- Borrowers cannot be extended more than two loans from different MFIs at the same time.
7. Regulations on NBFC for Sale
- Any NBFC for sale or transfer of ownership must be approved by the RBI.
- A due diligence process must be conducted to ensure compliance with RBI norms.
- The new buyer must meet the financial and regulatory requirements set by the RBI before taking over the NBFC.

Steps for Microfinance Company Registration in India
If you plan to start a microfinance business, you can register under two categories:
1. NBFC Microfinance Company Registration
To register an NBFC-MFI, follow these steps:
- Incorporate a Private/Public Limited Company under the Companies Act, 2013.
- Obtain a Certificate of Incorporation from the MCA.
- Ensure the minimum net owned fund requirement (₹5 crore or ₹2 crore in Northeast India).
- Prepare a business plan outlining lending models, compliance strategies, and operational structure.
- Submit an application to the RBI with all required documents.
- Obtain the Certificate of Registration (CoR) from RBI to commence operations.
- Register with a credit bureau for compliance with borrower loan limits.
2. Section 8 Microfinance Company Registration
For a Section 8 microfinance company, follow these steps:
- Obtain a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) and Director Identification Number (DIN) for directors.
- Apply for name approval through the MCA portal.
- Draft the Memorandum of Association (MOA) and Articles of Association (AOA) outlining the objectives.
- Apply for Section 8 License with the Registrar of Companies (RoC).
- File incorporation documents using SPICe+ Form on the MCA portal.
- Obtain PAN, TAN, and open a bank account for financial transactions.
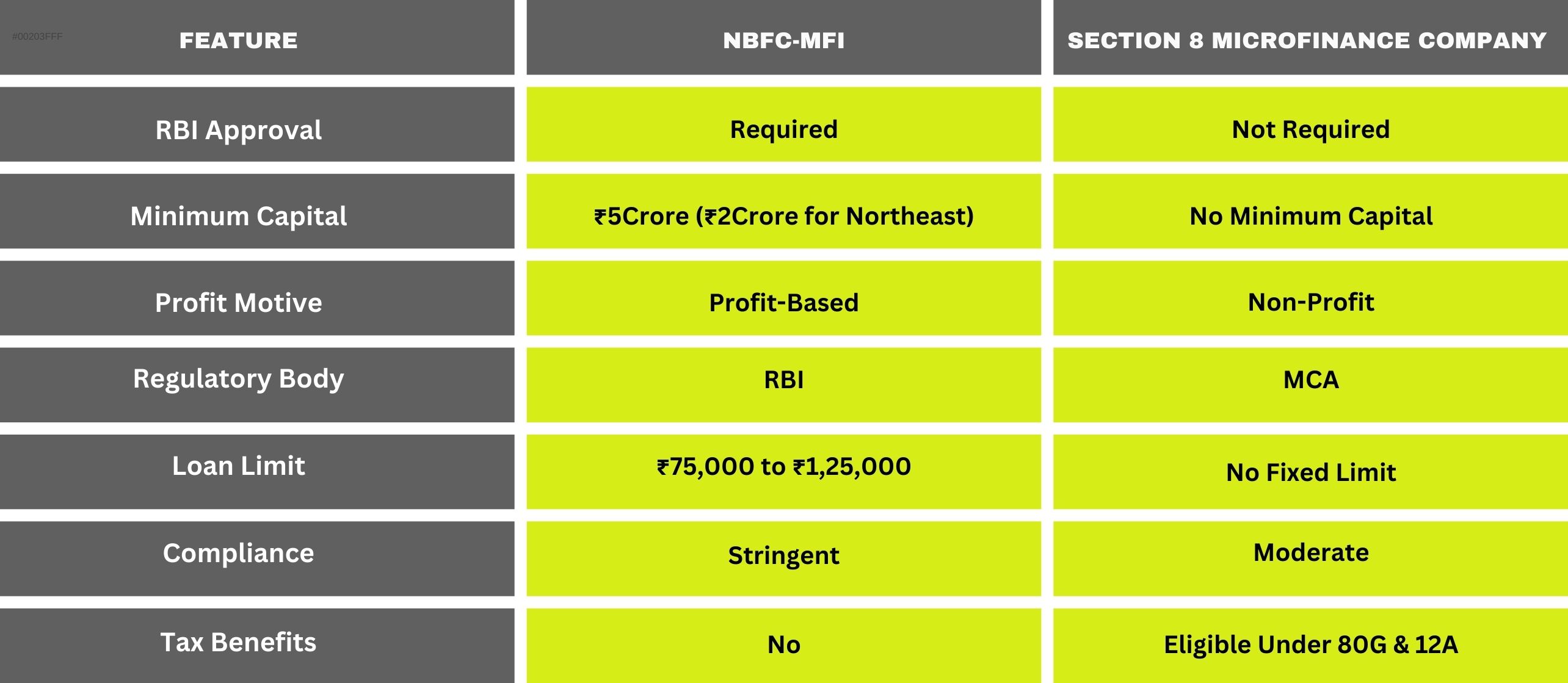
Comparison: NBFC vs. Section 8 Microfinance Company
Conclusion
For anyone looking to establish a microfinance company in India, understanding the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) guidelines is essential to ensure compliance, smooth operations, and long-term sustainability. The RBI has put in place specific regulations to govern microfinance institutions (MFIs) and safeguard both lenders and borrowers from financial risks and unethical lending practices. These guidelines help maintain financial stability, consumer protection, and transparency in the sector.
NBFC-MFI vs. Section 8 Microfinance Company: Choosing the Right Model
Microfinance companies can be structured in different ways, with two popular options being Non-Banking Financial Company – Microfinance Institution (NBFC-MFI) and Section 8 Microfinance Company.
- NBFC-MFI: This is a for-profit microfinance model that requires mandatory registration with the RBI. To operate as an NBFC-MFI, a company must have a minimum net owned fund (NOF) of ₹5 crore (₹2 crore for Northeast India) and comply with strict financial regulations, including lending caps, borrower limits, and interest rate guidelines. While this structure offers greater flexibility in lending and scaling operations, it involves a complex licensing process, ongoing compliance, and higher operational costs.
- Section 8 Microfinance Company: This is a non-profit model governed by the Companies Act, 2013, and regulated by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) instead of the RBI. Unlike NBFC-MFIs, Section 8 microfinance companies do not require RBI approval, making them a cost-effective and simpler alternative for those looking to engage in micro-lending for social impact. They enjoy tax exemptions under Sections 12A and 80G of the Income Tax Act and are a preferred choice for organizations focusing on financial inclusion without a profit motive.
If you are planning to start a microfinance business or are considering an NBFC for sale, it is essential to carefully evaluate your financial goals, compliance requirements, and regulatory responsibilities. NBFC-MFIs offer greater operational freedom but come with higher capital requirements and strict RBI oversight. In contrast, Section 8 microfinance companies are easier to set up and maintain, making them ideal for social entrepreneurs and NGOs looking to provide financial assistance without regulatory burdens.
By ensuring compliance with microfinance registration guidelines, you can build a legally sound and sustainable microfinance institution. Whether you opt for NBFC registration or Section 8 microfinance company registration, following the right regulatory framework will help you operate efficiently, gain trust among borrowers, and contribute to financial empowerment in underserved communities.
Why Choose Vakilkaro for Other Related Services?
Vakilkaro is a trusted platform offering comprehensive legal, financial, and compliance solutions tailored to businesses of all sizes. Whether you need assistance with section 8 microfinance company registrationtrademark registrationGST return filingand compliance, RBI licensing, or microfinance company setup, Vakilkaro ensures a seamless and hassle-free experience.
Key Reasons to Choose Vakilkaro:
✅ Expert Legal Guidance: Vakilkaro has a team of professionals with expertise in corporate law, taxation, and regulatory compliance.
✅ End-to-End Support: From documentation to approvals, Vakilkaro manages the entire process efficiently.
✅ Cost-Effective Solutions: Transparent pricing with no hidden charges makes it an affordable choice.
✅ Fast & Reliable Service: Quick turnaround time ensures smooth business operations without delays.
✅ Comprehensive Service Portfolio: One-stop solution for company formation, intellectual property protection, taxation, and legal documentation.
Vakilkaro simplifies complex processes, making it the ideal partner for businesses seeking professional, reliable, and efficient legal services.