Understanding Interest Rate Limits for Microfinance Companies
Microfinance companies play a vital role in providing financial assistance to low-income individuals and small businesses that lack access to traditional banking. These institutions, including Section 8 microfinance companies and Non-Banking Financial Company – Microfinance Institutions (NBFC-MFIs), operate under specific regulatory frameworks designed to ensure fair lending practices and prevent exploitation.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) governs NBFC-MFIs, setting limits on interest rates, processing fees, and penalties to maintain transparency and borrower protection. NBFC-MFIs can charge a maximum interest rate based on either 2.75 times the average base rate of major banks or a margin cap of 10-12%, depending on the size of the institution. Additionally, processing fees are capped at 1% of the loan amount, and prepayment penalties are prohibited. Section 8 microfinance companies, on the other hand, function as non-profit organizations and are not subject to RBI’s direct regulation. However, they must follow reasonable interest rate guidelines to ensure affordable credit access.
Several factors influence interest rate limits in microfinance, including the cost of borrowing, risk premiums due to unsecured lending, and high operational expenses in rural areas. While regulations help prevent unfair lending practices, they also pose challenges for microfinance institutions. Strict interest rate caps can affect profitability, limit access to credit for high-risk borrowers, and increase dependence on informal moneylenders.
To strike a balance, regulators are working on flexible frameworks that promote sustainable lending while protecting borrowers. Emphasizing technology-driven cost reductions, financial literacy programs, and fair lending practices will ensure microfinance continues to drive financial inclusion and economic empowerment. A well-regulated microfinance sector is essential for extending credit to underserved communities while maintaining financial stability.

Introduction
Microfinance companies play a vital role in providing financial services to low-income individuals and small businesses that lack access to traditional banking. These institutions offer small-ticket loans, enabling economic empowerment and financial inclusion. However, to ensure borrower protection and prevent exploitation, regulatory authorities impose interest rate limits on microfinance companies.
In India, microfinance institutions (MFIs) operate under two main categories: Section 8 microfinance company registration and Non-Banking Financial Companies – Microfinance Institutions (NBFC-MFIs). The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) sets specific regulations for interest limits in NBFC registration, ensuring fair lending practices and financial stability. This blog will explore the interest rate limits for microfinance companies, their regulatory framework, and how they impact borrowers and lenders.
Understanding Microfinance Companies
Microfinance companies provide small loans, typically without collateral, to individuals who need financial assistance for business, education, healthcare, or other essential needs. There are two primary types of microfinance companies in India:
1. Section 8 Microfinance Company
A Section 8 microfinance company is a non-profit entity registered under the Companies Act, 2013. It operates with a primary objective of providing microcredit to underserved communities without the motive of earning profits. Unlike NBFC-MFIs, Section 8 microfinance companies do not require NBFC registration but must comply with RBI guidelines on financial lending.
2. NBFC-MFI (Non-Banking Financial Company – Microfinance Institution)
An NBFC-MFI is a specialized non-banking financial company registered with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). It primarily lends to low-income individuals while adhering to specific interest rate limits and operational guidelines prescribed by the RBI.
Regulatory Framework for Microfinance Interest Rates
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) governs microfinance companies, particularly NBFC-MFIs, to ensure transparency and fair lending practices. Interest rate caps are imposed to prevent borrower exploitation while enabling MFIs to remain sustainable.
1. RBI’s Guidelines on Interest Rate Limits for NBFC-MFIs
For NBFC-MFIs, the RBI has set the following interest rate limits:
- Maximum Interest Rate: NBFC-MFIs are allowed to charge the lower of 2.75 times the average base rate of the five largest commercial banks or a margin cap of 10% for large MFIs (loan portfolios above ₹100 crore) and 12% for smaller MFIs.
- Processing Fee Cap: The processing fee should not exceed 1% of the loan amount.
- Penalty Restrictions: No prepayment penalty should be charged, and any penalty for delayed payment should only be on the overdue amount and not on the entire loan principal.
- Transparency Requirement: Loan terms, including effective interest rates, must be clearly communicated to borrowers in writing.
2. Interest Rate Guidelines for Section 8 Microfinance Companies
Unlike NBFC-MFIs, Section 8 microfinance companies do not fall under RBI’s strict regulatory framework. However, they must comply with the following guidelines:
- Loans should be provided at reasonable interest rates to ensure affordability.
- Interest rates should not exceed the rates charged by NBFC-MFIs.
- Section 8 companies must maintain transparency in loan disbursement and interest charges.
Factors Affecting Interest Rate Limits in Microfinance Companies
Several factors influence the interest limits in NBFC registration and lending rates of microfinance institutions:
1. Cost of Funds
The interest rates charged by microfinance companies are largely dependent on their cost of borrowing from financial institutions, banks, or investors. A higher cost of funds leads to higher lending rates.
2. Risk Premium
Microfinance loans are provided without collateral, making them high-risk. To compensate for the risk of non-repayment, MFIs include a risk premium in their interest rates.
3. Operational Costs
Microfinance institutions operate in rural and semi-urban areas, leading to higher operational costs due to staff salaries, loan disbursement, and collection expenses.
4. Borrower Profile
Microfinance borrowers generally have low credit scores or no formal credit history. As a result, MFIs must assess their repayment capacity carefully and adjust interest rates accordingly.
Comparison of Interest Rates: NBFC-MFIs vs. Section 8 Microfinance Companies
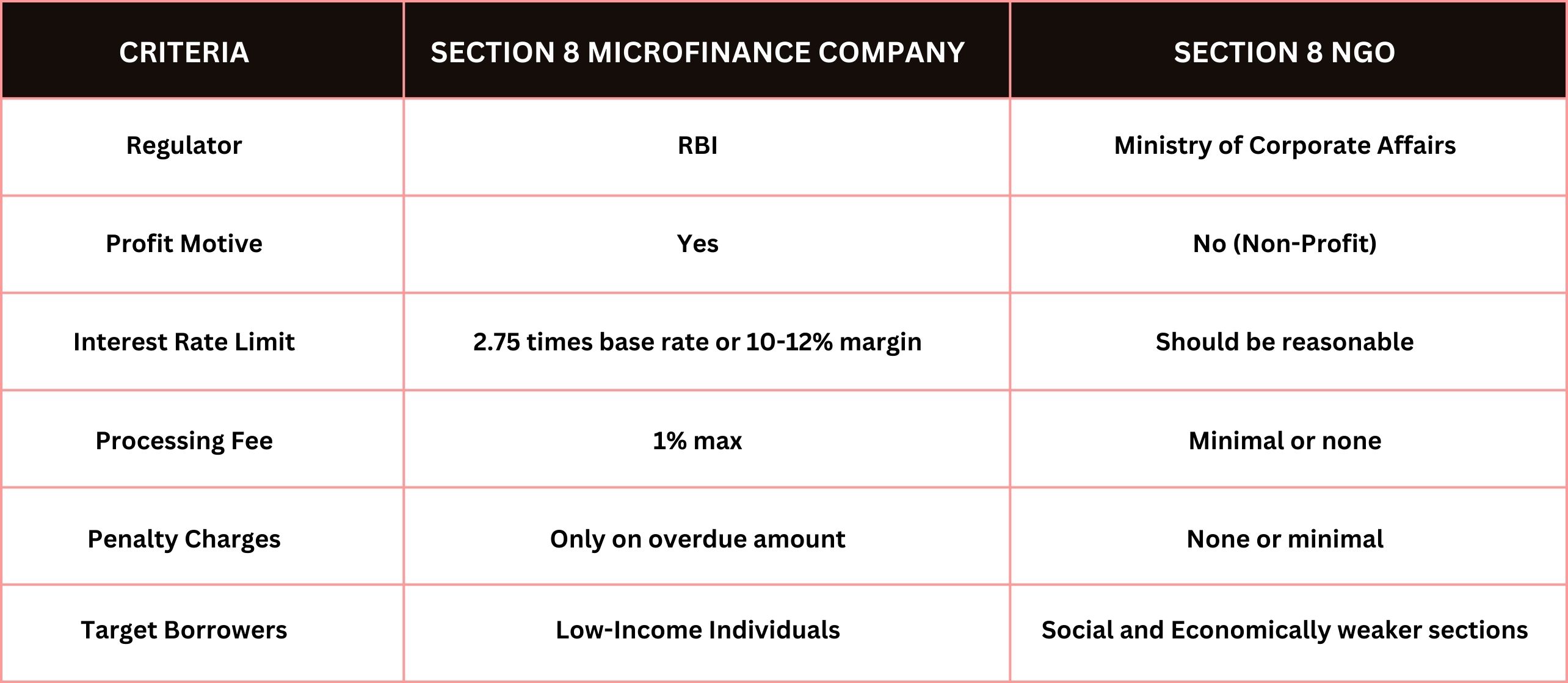
Challenges of Interest Rate Regulation in Microfinance
While interest rate limits protect borrowers, they also create challenges for microfinance companies:
1. Sustainability Issues
Strict interest rate caps can impact the profitability and sustainability of MFIs, making it difficult to cover operational costs.
2. Credit Access Limitation
If interest rates are set too low, microfinance institutions may limit lending to only the safest borrowers, excluding high-risk individuals who need credit the most.
3. Alternative Lending Channels
Excessive interest rate regulation can drive borrowers towards unregulated moneylenders who charge exorbitant interest rates without legal protections.
4. Administrative Burden
Maintaining compliance with RBI’s interest rate regulations requires regular monitoring, reporting, and adherence to documentation standards.
Future of Interest Rate Limits in Microfinance
The microfinance sector in India continues to evolve, with increasing efforts to balance borrower protection and financial institution sustainability. The RBI is working on dynamic regulatory frameworks to:
- Allow flexibility in interest rate determination based on market conditions.
- Encourage technology-driven cost reduction to improve lending efficiency.
- Promote financial literacy programs to help borrowers understand loan terms and interest rates better.
- Expand access to affordable credit while ensuring transparency and fair lending practices.
Conclusion
Interest rate limits in microfinance are crucial for ensuring fair lending and borrower protection. While NBFC-MFIs operate under RBI’s strict regulatory guidelines, Section 8 microfinance companies must adhere to reasonable interest rates. The interest limits in NBFC registration ensure that microfinance institutions charge fair rates while remaining financially viable.
Understanding these regulations helps microfinance institutions comply with legal requirements while continuing to serve low-income borrowers effectively. As the sector evolves, balanced regulations will ensure that microfinance remains a key driver of financial inclusion and economic empowerment in India.
Why Choose Vakilkaro for Legal and Financial Services?
Vakilkaro stands out as a trusted legal and financial service provider, offering a wide range of solutions tailored to businesses, startups, and individuals. With a strong reputation for professionalism, expertise, and client-centric services, Vakilkaro simplifies complex legal procedures, ensuring hassle-free compliance and seamless execution.
Comprehensive Service Portfolio
Vakilkaro provides expert assistance in company registration, trademark registration, GST compliance tax advisory, intellectual property protection, contract drafting, and legal documentation. Whether you need help with business licenses, RBI approvals, or corporate restructuring, Vakilkaro ensures accuracy and efficiency.
Expert Guidance and Legal Support
With a team of experienced legal professionals and financial experts, Vakilkaro offers precise guidance on regulatory requirements, ensuring compliance with laws governing businesses, taxation, and intellectual property rights. Their expertise in Section 8 microfinance registration, NBFC compliance, and corporate governance makes them a reliable partner for entrepreneurs.
Time-Efficient and Cost-Effective Solutions
Vakilkaro’s streamlined approach saves time and minimizes costs for clients. Their digital processes and dedicated support ensure quick application approvals, reducing delays in legal formalities.
Customer-Centric Approach
Vakilkaro prioritizes customer satisfaction by providing personalized solutions, transparent pricing, and dedicated support throughout the service process. Their commitment to simplifying legal complexities makes them the preferred choice for businesses and individuals seeking professional assistance.
By choosing Vakilkaro, clients gain access to reliable, efficient, and legally sound solutions that support business growth, legal protection, and financial stability. Whether for registrations, compliance, or legal documentation, Vakilkaro remains a trusted partner for diverse legal and financial needs.